In this tutorial, we will demonstrate how to exclude your WordPress admin area web traffic from Google Analytics.
Why exclude WordPress admin traffic from Google Analytics?
If you need to measure the real traffic to your website from your end users, you should exclude traffic from your logged-in WordPress users/administrators. This way, only the relevant traffic from the end users will be shown in Google Analytics reports.
Here are the steps you’ll need to follow to remove all the irrelevant traffic from logged-in WordPress users:
Step 1: Login to Google Analytics and go Pages Report
Login to Google Analytics on analytics.google.com, and navigate over to Behavior > Site Content > All Pages to access the Pages Report, as demonstrated below:
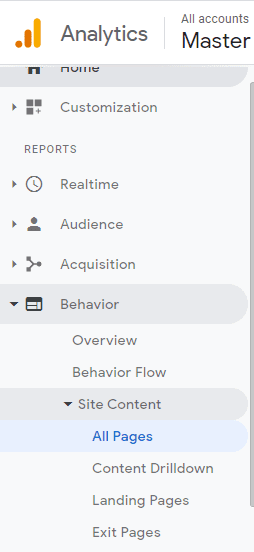
From the Pages Report, you’ll need to identify any irrelevant pages that you would like to exclude from Google Analytics.
Such pages include WordPress theme builder pages or WordPress pages that are visible only to logged-in WordPress users.
For example, in case of the Divi theme builder, you may be able to identify that “et_pb” appears in several page URIs.
Note down all such common URI/URL values that you want to exclude from Google Analytics.
Step 2: Go to View > Filters
After you have identified the URI values that you need to exclude from the Analytics reports, click the gear icon, which will take you to the Admin area.
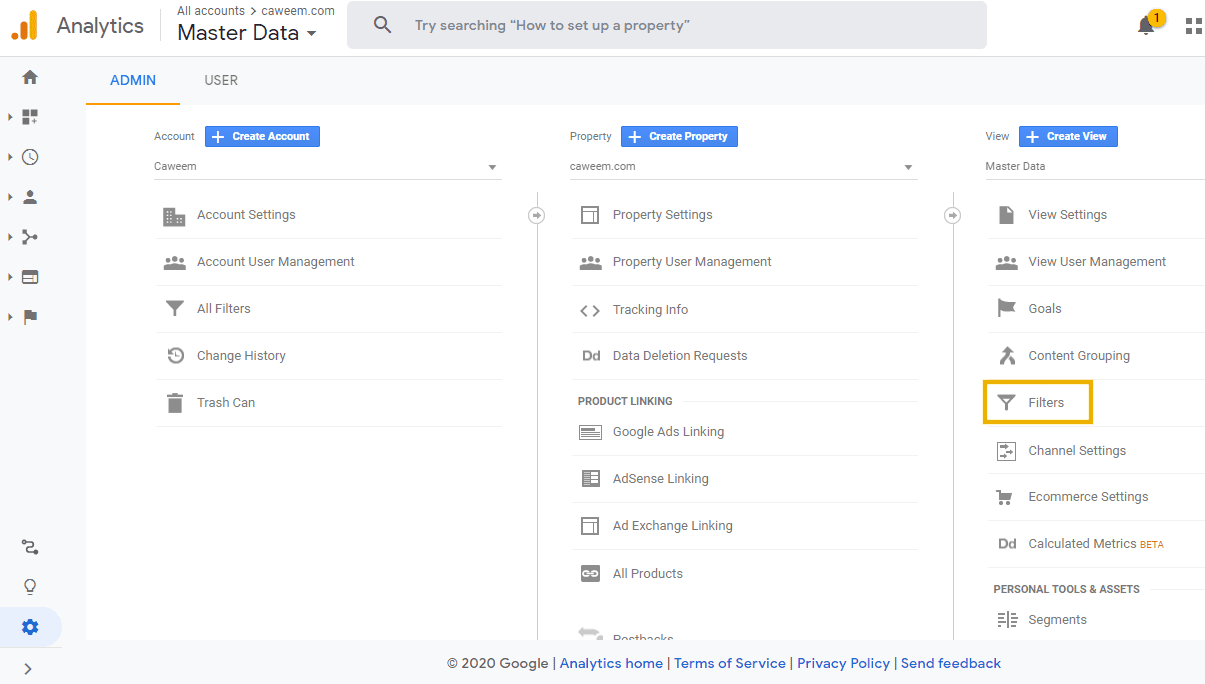
On the Admin dashboard, navigate to the Filters option under View, as shown above.
Step 3: Add Filters to exclude wp-login.php
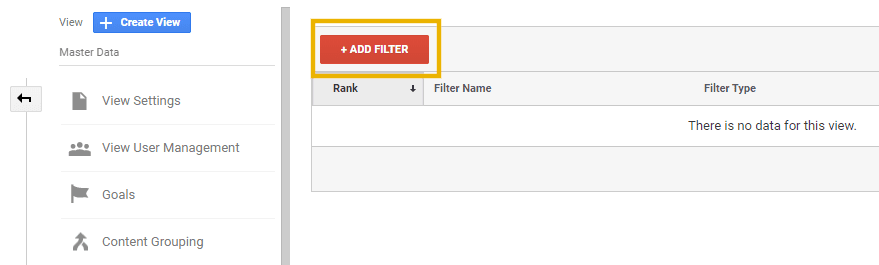
In addition to the URI values that you have identified in step 1, we will also specify some values that you should filter out of Google Analytics. The first of these is wp-login.php.
To exclude this URI, Add a Filter, as shown below.
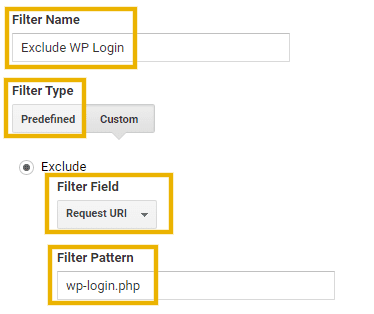
Create a new filter with the following details:
- Filter Name: Exclude WP Login
- Filter Type: Predefined
- Exclude
- Filter Field: URI
- Filter Pattern: wp-login.php
These steps are shown below.
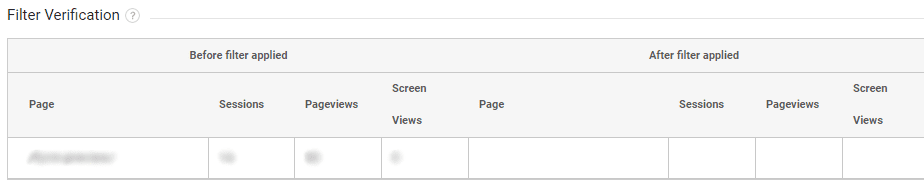
You can then click on “Verify this Filter” to test if it achieves the results you desire.
On doing so, you may get an output that shows how future data will be filtered out, as shown below.
Click Save to allow the changes to take effect.
Step 4: Add Filters to exclude wp-admin
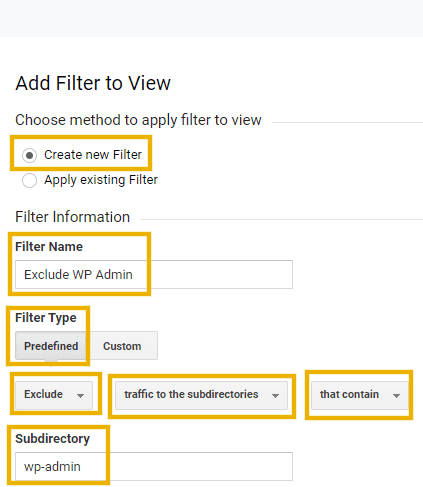
Now, we will need to filter out pages that contain wp-admin in the URL. To do this, create a new filter with the following details:
- Filter Name: Exclude WP Admin
- Filter Type: Predefined, Exclude, traffic to the subdirectories, that contain
- Subdirectory: wp-admin
Click Save to add this filter.
The above steps are illustrated in the screenshot below.
Step 5: Add Filters to exclude theme builder pages and other irrelevant pages
In a similar way to how we have filtered out wp-admin, we can also filter out any values that are associated with any WordPress live page builder, in case if you are using one.
You should have identified any such values in Step 1 above.
If you are not using a page builder, you may skip this step.
For the purposes of this tutorial, we will consider the example of the Divi builder, which may have values in the URL like “et_pb”.
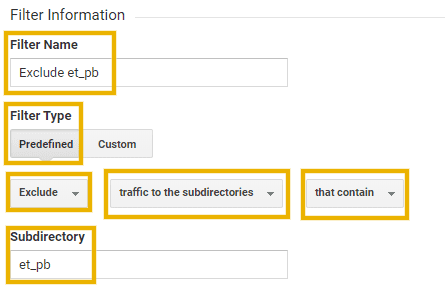
To exclude all page URLs/URIs that contain this value, create a new filter with the following details:
- Filter Name: Exclude et_pb
- Filter Type: Predefined, Exclude, traffic to the subdirectories, that contain
- Subdirectory: et_pb
Click Save to add this filter.
The above steps are demonstrated in the screenshot below.
Conclusion
Tip: Make sure that you are also filtering out All Bot Traffic if you intend to analyze data from real web users only.


I found the information you shared helpful. Thanks